Now Reading: Preventing Electrical Fires at Home and Work
-
01
Preventing Electrical Fires at Home and Work
Preventing Electrical Fires at Home and Work

Electricity is an essential part of modern life, powering our homes and businesses around the clock. However, this convenience comes with a significant risk. Electrical failures are a leading cause of property damage, and tragically, can result in serious injury or death. Understanding the dangers and taking proactive steps is crucial for protecting your family, employees, and assets.
Common Causes of Electrical Fires
Awareness is the first step toward prevention. Most electrical fires stem from issues that are often overlooked but can be easily addressed. Here are some of the most frequent culprits:
Faulty Outlets and Old Wiring
Outdated or damaged wiring is a major fire hazard. Over time, the insulation on wires can degrade, exposing the metal conductor and increasing the risk of arcing—a high-power discharge of electricity between conductors that can ignite nearby materials. This is particularly common in older buildings that may not have been updated to handle the electrical loads of modern appliances. Similarly, loose or malfunctioning outlets can overheat and spark, igniting dust or other flammable materials.
Overloaded Circuits and Extension Cords
Every electrical circuit is designed to handle a maximum amount of electricity. When you plug too many devices into a single circuit or use extension cords to power multiple high-wattage appliances, you can cause an overload. This excess electrical current generates heat, which can melt the wire insulation and lead to a fire. Using extension cords as a permanent wiring solution is particularly dangerous, as they are not designed for long-term, heavy use.
Malfunctioning Appliances and Equipment
Appliances with frayed cords, damaged plugs, or internal electrical problems pose a serious risk. Overheating is a common issue, especially in devices with motors like refrigerators or air conditioners. When these appliances are not properly maintained or are used incorrectly, they can short-circuit and ignite. It’s also important to ensure that appliances have adequate ventilation, as blocking air vents can cause them to overheat.
Improper Use of Lighting
Light bulbs and fixtures also contribute to electrical fires. Using a light bulb with a higher wattage than a fixture is rated for can cause the fixture to overheat, melting the socket and insulation on the wiring. Another hazard is placing flammable materials like cloth or paper too close to a hot light bulb. Portable lamps can also be a risk if they are knocked over, bringing the hot bulb into contact with flammable surfaces like carpets or bedding.
Prevention Tips for Homeowners

Protecting your home from electrical fires involves regular maintenance and safe practices. Here are actionable steps every homeowner can take:
- Inspect Cords and Plugs: Regularly check all electrical cords for signs of fraying, cracking, or damage. Replace any cords that are not in perfect condition. Ensure plugs fit snugly into outlets and are not loose.
- Avoid Overloading Outlets: Don’t plug multiple high-power appliances into a single outlet or extension cord. Distribute your electrical load across different circuits. Unplug small appliances like toasters and coffee makers when not in use.
- Use Extension Cords Safely: Extension cords should only be a temporary solution. Never run them under carpets or through doorways where they can be damaged. Use cords that are rated for the power of the devices you are plugging into them.
- Check Your Light Fixtures: Always use light bulbs that match the recommended wattage for your lamps and fixtures. Keep flammable materials away from light bulbs.
- Update Your Electrical System: If you live in an older home, consider having a qualified electrician inspect your wiring. Upgrading your electrical panel, outlets, and wiring can significantly reduce your fire risk.
Prevention Tips for Businesses

For businesses, the stakes are even higher due to the presence of employees, customers, and valuable assets. Commercial properties often have more complex electrical systems that require professional oversight.
- Schedule Regular Electrical Inspections: Hire a licensed electrician, like an industrial electrician in Michigan, to conduct annual inspections of your entire electrical system. This helps identify potential issues before they become serious hazards.
- Ensure Proper Equipment Maintenance: All electrical equipment, from computers to machinery, should be regularly maintained according to manufacturer guidelines. Immediately repair or replace any equipment with faulty wiring or signs of overheating.
- Train Your Employees: Educate your staff on electrical safety best practices. This includes knowing how to properly use equipment, recognizing warning signs like burning smells or flickering lights, and understanding emergency procedures.
- Maintain Clearances Around Electrical Panels: Keep the area around your electrical panels clear of clutter and obstructions. This ensures easy access in an emergency and prevents flammable materials from being stored too close to a potential ignition source.
- Install and Test AFCI Outlets: Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs) are designed to detect dangerous arcing and shut off power to the circuit before a fire can start. These are particularly important in commercial settings.
Advanced Fire Safety Measures
Beyond basic prevention, you can invest in advanced systems to enhance the safety of your home or business. These technologies provide an extra layer of protection against electrical fires.
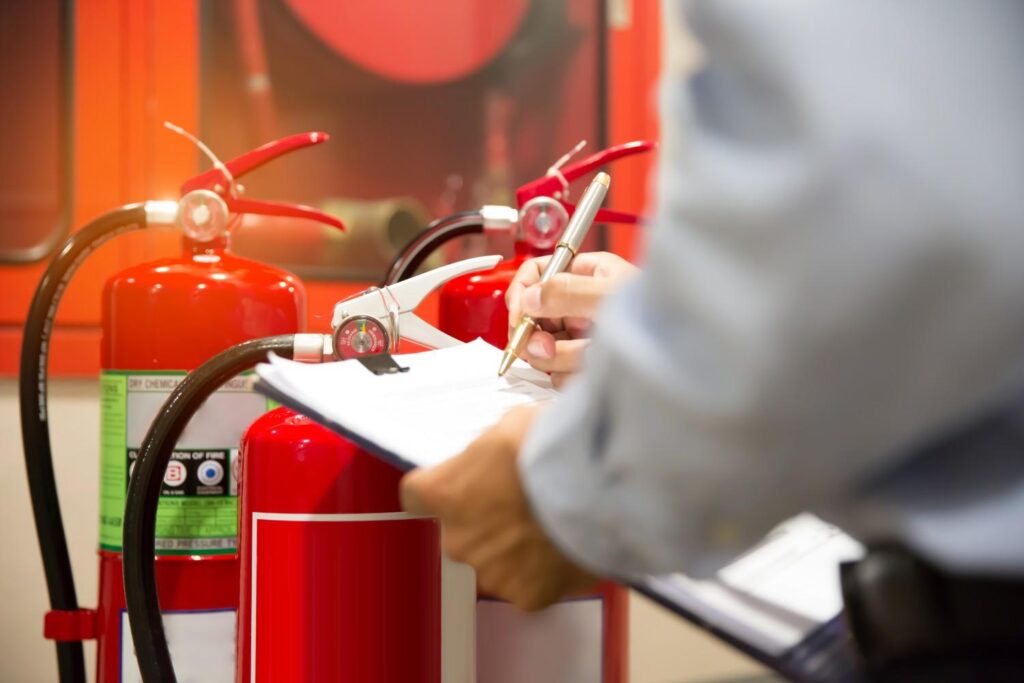

Smoke and Heat Detectors
Smoke detectors are your first line of defense. Install them in every bedroom, outside each sleeping area, and on every level of your property. For added protection, consider interconnected alarms that all sound when one is triggered. Heat detectors are also beneficial in areas like kitchens and garages, where smoke from cooking can cause false alarms. Test all detectors monthly and replace the batteries at least once a year.
Fire Extinguishers
Having the right type of fire extinguisher and knowing how to use it can stop a small fire from becoming a catastrophe. For electrical fires, you need a Class C or multi-purpose (ABC) extinguisher. Place extinguishers in easily accessible locations, especially in the kitchen and garage. Ensure family members or employees are trained on the PASS method: Pull, Aim, Squeeze, and Sweep.
Professional Electrical Audits
For both older homes and all commercial properties, a professional electrical audit is a wise investment. An electrician will conduct a thorough examination of your entire system, from the service panel to the individual outlets. They can identify code violations, safety risks, and opportunities for energy efficiency improvementsenergy efficiency improvements. This comprehensive check provides peace of mind and a clear action plan for any necessary upgrades.
Conclusion
Electrical fires can be prevented. You can significantly lower the risk to your property and loved ones by understanding common causes and using consistent safety practices. Regular inspections, responsible appliance use, and proper training are essential parts of a strong fire safety plan.












